Bulk short read services
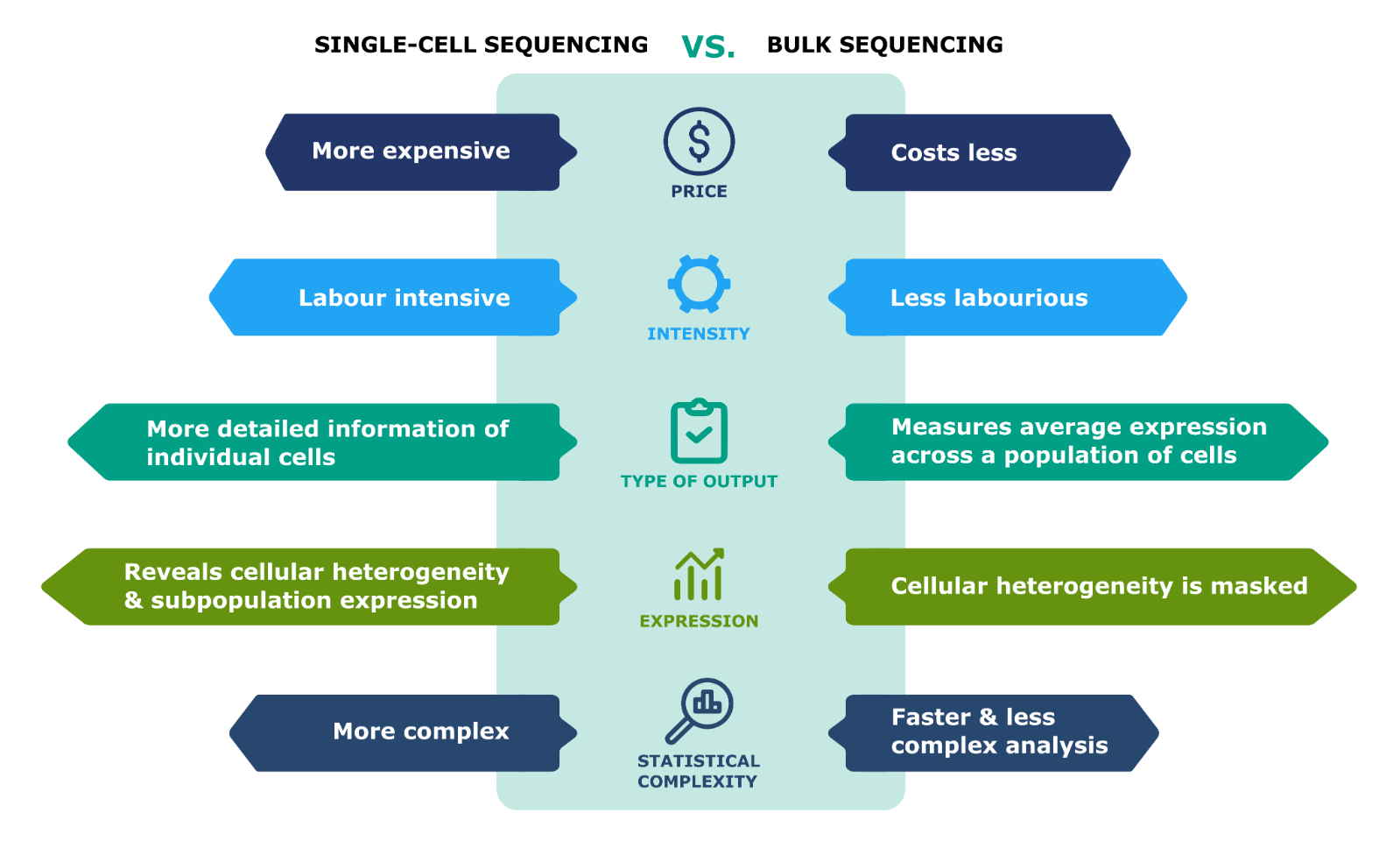
Bulk Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) refers to high-throughput sequencing techniques that analyse genetic material from a population of cells or organisms, providing a comprehensive view of the genetic makeup, gene expression, or epigenetic modifications across the sampled population.
Key Advantages of Bulk NGS:
- High-throughput: Capable of sequencing millions to billions of DNA or RNA fragments simultaneously.
- Cost-effective: More affordable than traditional methods when sequencing large genomes or many samples.
- Comprehensive: Provides a broad overview of genetic information, capturing a wide range of variations and expression profiles.
Limitations:
- Loss of Cellular Resolution: Bulk NGS provides averaged data across all cells in the sample, which can mask the heterogeneity present in cell populations.
- Requires High-Quality DNA/RNA: Degraded samples can lead to incomplete or biased sequencing data.
 Credit: BioLizard
Credit: BioLizard
Below is a brief overview of the main types of bulk NGS methods:
1. Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS)
- Purpose: Provides a complete DNA sequence of an organism's genome.
- Applications: Identifying genetic variations, studying evolutionary relationships, and detecting rare mutations.
- Process: All genomic DNA is fragmented, sequenced, and then assembled to represent the entire genome.
- GCTU Services: KAPA DNA HyperPrep, Illumina DNA Prep, Custom kit, Sequencing Only
2. Whole Exome Sequencing (WES)
- Purpose: Focuses on sequencing the exonic regions of the genome, which code for proteins.
- Applications: Detecting mutations that affect protein-coding genes, particularly in genetic diseases.
- Process: Captures and sequences only the exome, which is about 1-2% of the genome.
- GCTU Services: Illumina RNA Prep with Exome Enrichment, Custom kit, Sequencing Only
3. Targeted Sequencing
- Purpose: Sequences specific regions of the genome, such as a panel of genes of interest.
- Applications: Diagnosing genetic disorders, validating mutations, or studying specific pathways.
- Process: Uses probes to capture and sequence only the targeted regions.
- GCTU Services: Custom kit, Sequencing Only
4. RNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq)
- Purpose: Quantifies gene expression by sequencing RNA, providing a snapshot of the transcriptome.
- Applications: Studying gene expression profiles, alternative splicing, and identifying novel transcripts.
- Process: RNA is converted to cDNA, which is then sequenced and mapped to the genome to quantify expression levels.
- GCTU Services: KAPA RNA HyperPrep (ribodepletion from Human, Mouse, Rat or Bacteria using Illumina RiboZero), QuantSeq 3' FWD, Custom kit, Sequencing Only
5. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Sequencing (ChIP-Seq)
- Purpose: Identifies the binding sites of DNA-associated proteins, such as transcription factors.
- Applications: Studying protein-DNA interactions, epigenetic regulation, and identifying regulatory elements.
- Process: Chromatin is immunoprecipitated using antibodies against a specific protein, and the bound DNA is sequenced.
- GCTU Services: Sequencing Only
6. Bisulfite Sequencing (BS-Seq)
- Purpose: Maps DNA methylation patterns across the genome.
- Applications: Studying epigenetic modifications and their impact on gene expression and disease.
- Process: DNA is treated with bisulfite, converting unmethylated cytosine to uracil, while methylated cytosine remains unchanged, and then sequenced.
- GCTU Services: Twist Human Methylome kit, Sequencing Only
7. ATAC-Seq (Assay for Transposase-Accessible Chromatin with high-throughput sequencing)
- Purpose: Identifies open chromatin regions, indicating active regulatory elements.
- Applications: Studying chromatin accessibility, gene regulation, and enhancer activity.
- Process: Tn5 transposase inserts sequencing adapters into accessible chromatin regions, which are then sequenced.
- GCTU Services: Sequencing Only
8. Shotgun Metagenomics
- Purpose: Sequences the collective DNA from a mixed community of organisms, typically microbial communities.
- Applications: Characterising microbial diversity, studying microbial functions, and exploring the interactions within ecosystems (e.g., human gut microbiome, soil microbiome).
- Process: All DNA from an environmental sample is fragmented and sequenced randomly (shotgun approach), allowing for the identification and quantification of different organisms and their genetic content.
- GCTU Services: Illumina DNA Prep, KAPA DNA HyperPrep, Custom kit, Sequencing Only
9. Small RNA Sequencing
- Purpose: Specifically sequences small RNA molecules, such as microRNAs (miRNAs), small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), and Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs).
- Applications: Studying gene regulation, identifying novel small RNAs, and understanding RNA interference and other post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms.
- Process: Small RNAs are isolated, converted to cDNA, and then sequenced to identify and quantify these regulatory molecules.
- GCTU Services: Qiagen miRNA kit, Custom kit, Sequencing Only
Bulk NGS methods are foundational in genomics, enabling wide-ranging applications from basic research to clinical diagnostics. Please visit our Services page to see our off the shelf bulk sequencing services. We also offer a 'Sequencing Only' service for user prepared NGS libraries.
We can also perform any library preparation method required under our 'Custom' route - please reach out to genomics@qub.ac.uk to discuss.